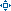
|
Contaminant
|
Potential Side Effect
|
How did that get in my water?
|
|
Arsenic
|
Increased risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, immunological disorders, diabetes and other medical issues
|
Naturally occurring throughout New England and NH; may also be result of pesticide use or coal ash disposal
|
|
Asbestos
|
Increased risk of intestinal polyps
|
Decay of asbestos cement in water mains and/or erosion of natural deposits
|
|
Barium
|
Increased blood pressure
|
Discharge from metal refineries, erosion of natural deposits, or discharge of drilling wastes
|
|
Bromate
|
Increased risk of cancer
|
Bromate is a byproduct of some methods of water disinfection
|
|
Cadmium
|
Kidney damage
|
Corrosion of galvanized pipes, runoff from waste batteries and paints, or erosion of natural deposits
|
|
Chlorine/C12
|
Eye/nose irritant; stomach discomfort; anemia
|
Chlorine is an additive used to control microbes
|
|
Coliform Bacteria
|
Full analysis needed to determine if disease organisms may be present in water; no threat in itself
|
Indicator organisms, caused by possible presence of other disease organisms
|
|
Copper
|
Gastrointestinal distress, liver and kidney damage, Wilson’s Disease
|
Corrosion of household plumbing systems or erosion of natural deposits
|
|
E.Coli Bacteria
|
Stomach discomfort and illness
|
Human and animal wastes entering the water system
|
|
Fluoride
|
Bone disease, mottled teeth
|
Public water systems often add fluoride to promote strong teeth
|
|
Hardness
|
Water taste, mineral deposits on tubs/showers & dishes, reduction of heating efficiency, reduction of soap suds
|
Presence of excessive dissolved mineral in water
|
|
Iron
|
Staining on laundry and water fixtures; can clog pumps, strainers, and valves; metallic taste; may support the growth of bacteria
|
Dissolves into groundwater as acidic rain percolates through soil and rock
|
|
Lead
|
Children: Delays in physical or mental development; learning disabilities; attention deficit
Adults: kidney problems; high blood pressure
|
Corrosion of household plumbing systems; erosion of natural deposits
|
|
Manganese
|
Staining on laundry and water fixtures; can clog pumps, strainers, and valves; metallic taste; may support the growth of bacteria
|
Dissolves into groundwater as acidic rain percolates through soil and rock
|
|
Mercury
|
Kidney damage
|
Discharge from refineries and factories; runoff from landfills and croplands
|
|
Nitrate
|
Infants under six months who ingest water containing excessive levels of nitrogen compounds could become seriously ill and, if untreated, may die. Symptoms include shortness of breath and blue baby syndrome
|
Runoff from fertilizer use; leaching from septic tanks, sewage; erosion of natural deposits
|
|
Nitrite
|
Infants under six months who ingest water containing excessive levels of nitrogen compounds could become seriously ill and, if untreated, may die. Symptoms include shortness of breath and blue baby syndrome
|
Runoff from fertilizer use; leaching from septic tanks, sewage; erosion of natural deposits
|
|
pH
|
Low pH indicates acidic water, which may corrode pipes. May also cause green staining in showers or tubs.
|
The acidity or alkalinity of water
|
|
Radon
|
Increased risk of cancer
|
Erosion of natural deposits into well water; also found in building material
|
|
Sodium & Chloride
|
Possible slight increase in daily sodium intake
|
Naturally occurring around seacoast areas; also caused by road salt, water softener discharge, human/animal waste disposal, & leachate from landfills
|
|
Sulfide
|
Water odor
|
Decomposition of organic materials; chemical reactions of soil and bedrock minerals containing sulfur
|
|
Turbidity
|
Cloudiness in water; higher levels of turbidity are often associated with higher levels of disease causing microorganisms, such as viruses, parasites, and some bacteria
|
Soil runoff
|
|
Uranium
|
Increased risk of cancer
|
Erosion of natural deposits
|